AI发展的越来越好了,连我这种完全不了解python的人都稍微了解了一些,而且入门难度好低。不由得感叹 文章有点长 看完
1,先去httPs://www.python.org/ 安装好环境
2,Visual Studio Code – Code Editing. Redefined 安装vs code 这个也是免费好用的工具,可以让我这种小白清晰可见代码,代码可视化
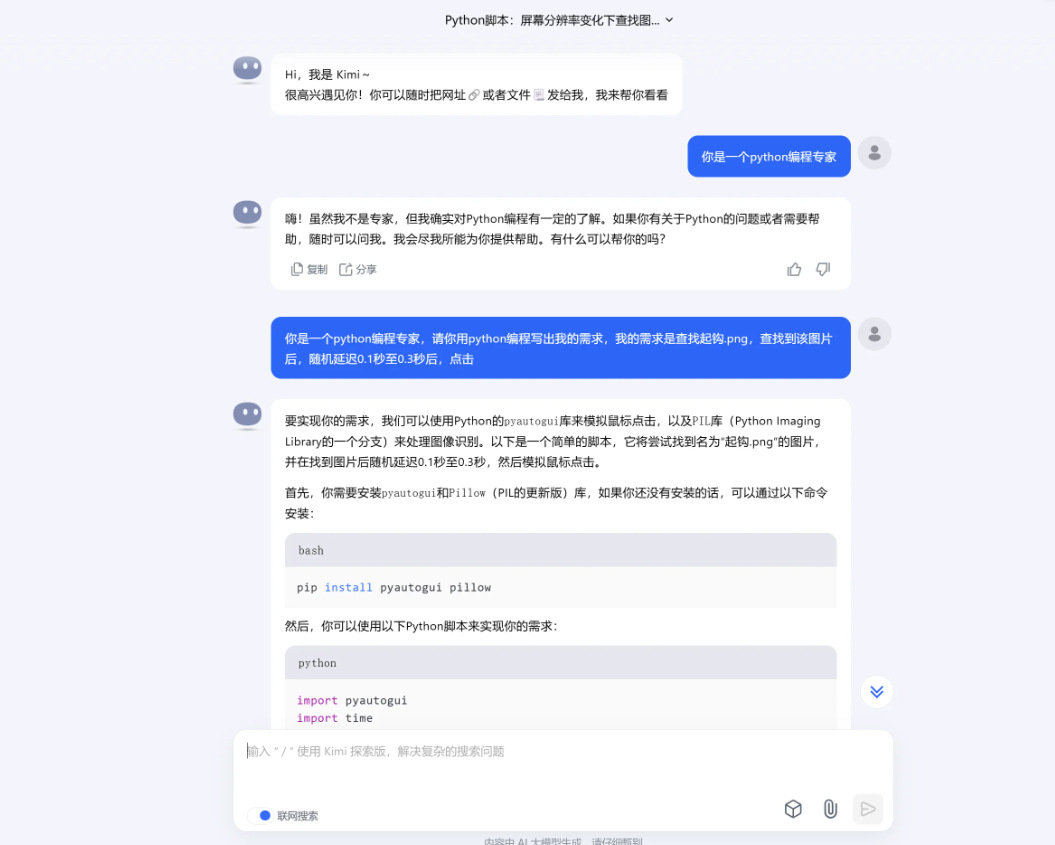
接下来就是开始使用kimi,以及豆包两种AI去直接提出我们的需求,比如我需要它给我一段 简单的识别屏幕图像 然后去点击,也就是挂机脚本。
import pyautogui
import time
import random
from PIL import ImageGrab
def find_image(image_path):
"""在屏幕上查找图片的位置"""
screenshot = ImageGrab.grab()
try:
image_location = pyautogui.locateOnScreen(image_path, confidence=0.8)
return image_location
except pyautogui.ImageNotFoundException:
return None
import pyautogui
import time
import random
from PIL import ImageGrab
def click_image(image_path):
"""查找图片并点击"""
image_location = find_image(image_path)
if image_location:
print(f"图片 {image_path} 找到,位置:{image_location}")
# 随机延迟0.1秒至0.3秒
time.sleep(random.uniform(0.1, 0.3))
# 点击图片位置
pyautogui.click(image_location)
print("点击图片")
else:
print(f"图片 {image_path} 未找到")
# 使用函数
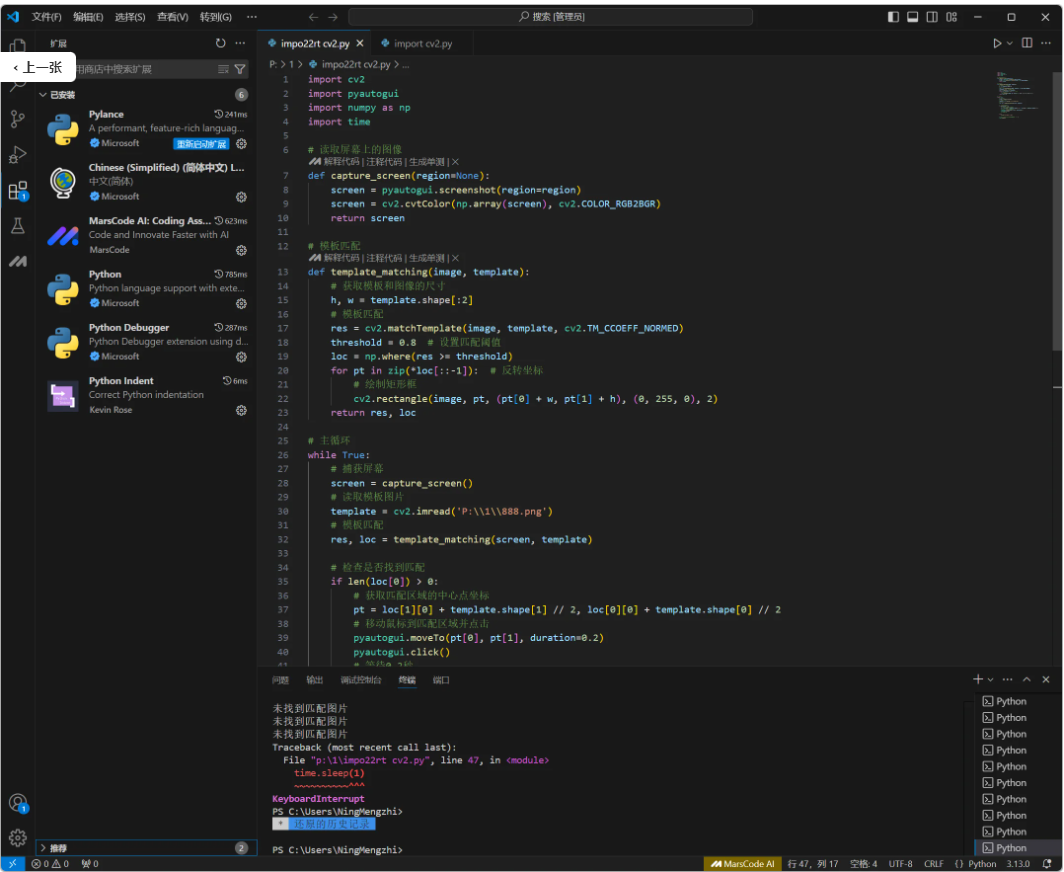
click_image('起钩.png')我们提出的问题,AI给出的答案是大概的,其中详细的参数需要自己填写,复制上面这段代码进入vs code,新建一个python文件,粘贴,运行会报错,因为需要的库没有安装
import pyautogui
import time
import random
from PIL import ImageGrab
在vs code调试输出处会直接给出安装库命令,非常好用,只不过安装源不是国内,你只需要复制vs code提出的建议命令到 kimi/豆包 AI,举例子:import pyautogui 帮我替换国内的源
如果需要写一个简单的挂机脚本
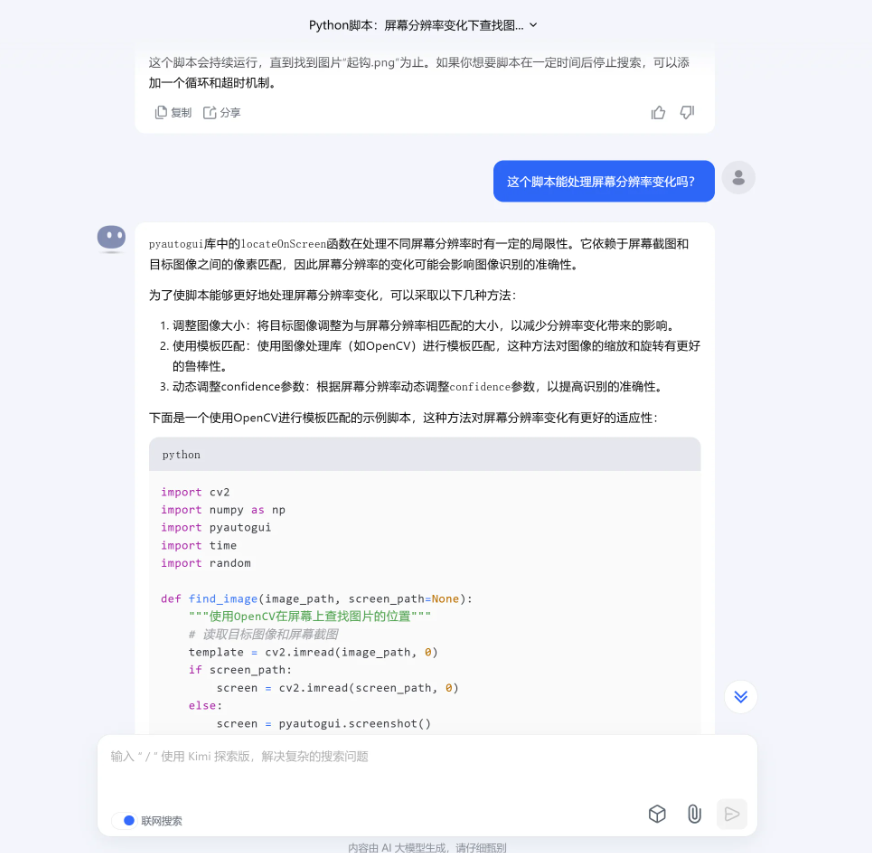
上方的图片给出的运行库是OpenCV,这个就比pyautogui强。
举例子 提出的问题是 用CV2库写一段代码图像识别代码,循环查找P:/1/1.png,如果找到P:/1/1.png,则0.2秒延迟后再移动到x=541, y=1587点击一次,点击后移动鼠标到x=541, y=1087循环结束,再进入下一个循环,同时循环查找P:/1/111.png和P:/1/5.png,如果找到的是P:/1/111.png,则0.2秒延迟后鼠标移动到x=541, y=1587点击一次,1秒延迟后移动鼠标到x=559, y=1832点击一次,0.2秒延迟后移动鼠标到x=541, y=1087,如果找到的是P:/1/5.png,则0.2秒延迟后鼠标移动到x=541, y=1587点击一次,1秒延迟后移动鼠标到x=559, y=1832点击一次,0.2秒延迟后移动鼠标到x=541, y=1087
import pyautogui import cv2 import numpy as np import time from pynput.keyboard import Listener, Key def find_image(image_path): """使用OpenCV查找屏幕上的图片并返回其位置""" screen = pyautogui.screenshot() screen = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(screen), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) image = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # 读取彩色图像 res = cv2.matchTemplate(screen, image, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED) threshold = 0.8 loc = np.where(res >= threshold) if len(loc[0]) > 0: # 返回第一个匹配的位置 top_left = loc[1][0], loc[0][0] return top_left else: print(f"未找到图片:{image_path}") return None # 监听键盘事件 - 这是额外添加的,你只需要对AI说防止这段程序无限循环- def on_press(key): global running if key == Key.esc: running = False def on_release(key): if key == Key.esc: return False # 主循环 running = True listener = Listener(on_press=on_press, on_release=on_release) listener.start() while running: # 循环查找P:/1/1.png found = False while not found: location_1 = find_image('P:/1/1.png') if location_1: time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.click(541, 1587) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.moveTo(541, 1087) # 移动到指定位置 found = True # 找到图片,退出循环 else: time.sleep(0.3) # 未找到图片,继续查找 # 循环查找P:/1/111.png和P:/1/5.png found = False while not found: location_111 = find_image('P:/1/111.png') location_5 = find_image('P:/1/5.png') if location_111: time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.click(541, 1587) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(1) # 1秒延迟 pyautogui.click(559, 1832) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.moveTo(541, 1087) # 移动到指定位置 found = True # 找到图片,退出循环 elif location_5: time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.click(541, 1587) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(1) # 1秒延迟 pyautogui.click(559, 1832) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.moveTo(541, 1087) # 移动到指定位置 found = True # 找到图片,退出循环 else: time.sleep(0.3) # 未找到图片,继续查找 listener.stop() 移动某个窗口到固定的坐标
简单的挂机脚本结合上面那段代码即可运行,坐标需要自己调试一下
import pyautogui import cv2 import numpy as np import time from pynput.keyboard import Listener, Key import pygetwindow as gw # 获取窗口 window = gw.getWindowsWithTitle('MuMu模拟器12')[0] # 假设只有一个窗口名为"MuMu模拟器12" # 移动窗口到左上角 window.moveTo(0, 0) # 获取窗口的大小 width, height = window.size # 打印窗口的大小和坐标 print(f"窗口大小:{width}x{height}") print(f"窗口坐标:{window.left},{window.top}") def find_image(image_path): """使用OpenCV查找屏幕上的图片并返回其位置""" screen = pyautogui.screenshot() screen = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(screen), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) image = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # 读取彩色图像 res = cv2.matchTemplate(screen, image, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED) threshold = 0.8 loc = np.where(res >= threshold) if len(loc[0]) > 0: # 返回第一个匹配的位置 top_left = loc[1][0], loc[0][0] return top_left else: print(f"未找到图片:{image_path}") return None # 监听键盘事件 def on_press(key): global running if key == Key.esc: running = False def on_release(key): if key == Key.esc: return False # 主循环 running = True listener = Listener(on_press=on_press, on_release=on_release) listener.start() while running: # 循环查找P:/1/1.png found = False while not found: location_1 = find_image('P:/1/1.png') if location_1: time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.click(541, 1587) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.moveTo(541, 1087) # 移动到指定位置 found = True # 找到图片,退出循环 else: time.sleep(0.3) # 未找到图片,继续查找 # 循环查找P:/1/111.png和P:/1/5.png found = False while not found: location_111 = find_image('P:/1/111.png') location_5 = find_image('P:/1/5.png') if location_111: time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.click(541, 1587) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(1) # 1秒延迟 pyautogui.click(559, 1832) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.moveTo(541, 1087) # 移动到指定位置 found = True # 找到图片,退出循环 elif location_5: time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.click(541, 1587) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(1) # 1秒延迟 pyautogui.click(559, 1832) # 点击指定位置 time.sleep(0.2) # 0.2秒延迟 pyautogui.moveTo(541, 1087) # 移动到指定位置 found = True # 找到图片,退出循环 else: time.sleep(0.3) # 未找到图片,继续查找
即使不会python,也没关系,报错,不明白的命令也直接问AI。





还没有评论,来说两句吧...